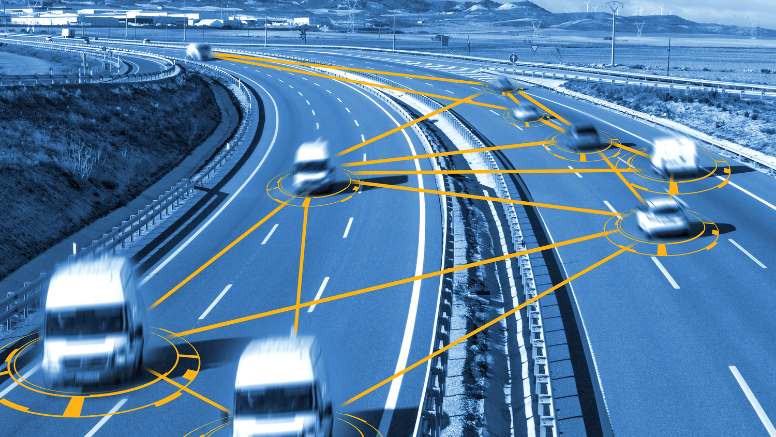
There is almost no aspect in today’s developed world that does not have technological interference in its design. Dependence on technology is such that it is required in every aspect of our lives and automobiles are no exception. The Automobile industry is one of the first industries which brought software aspects into its design to provide state-of-the-art facilities to people. From being just a mode of transportation from one place to another, they have taken the experience of traveling to another level with the help of technological advancements. But along with the advantages of technologically savvy features comes the risks too. The need for cyber security compliance is high here as the risk associated with each and every code installed into these automobiles is also high.
When it comes to cyber risk in automobiles, it might seem like it is associated with just the vehicle but the actual threat is to the user. This kind of threat is more when the automotive vehicle is an autonomous or connected car.
So how serious are these threats, how important is cyber security for the automobile industry, and what are the quick fixes and long-term solutions to the cyber risk present in evolving automobile technology? Read through to find out…
Role of Cyber security in the automotive industry
As already mentioned, major advancements in the automobile industry have been contributions from the field of technology. According to recent research, the E/E component market in the automobile industry is expected to grow USD 469 billion in the next 10 years. This simply means that the cyber risks associated with this industry are also expected to grow. Let us consider the possible kinds of cyber threats that can arise from these advancements:
- 1. Risks associated with connected cars: Tools like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are major contributors to communication devices and automobiles have adapted to equipping these features. Hackers are on the constant lookout for cloud networks when to gain access to the chain of vehicles connected to cloud networks through these tools. There are various technologies like vehicle to vehicle, vehicle to cloud, etc. for enabling this threat.
- 2. Risk associated with autonomous vehicles: Autonomous vehicles need sensors within for functioning and they are dependent on data networks present around them like GPS. Any attack potentially can harm their functioning and lead to accidents. Although these seem straight out of fiction, without proper cyber security they will not be safe to function.
- 3. Risks associated with electric vehicles: Electric vehicles need charging stations for consistent functioning. Any cyber-attacks on the charging stations or infrastructure can collapse the vehicle and lead to a power accident. This is a major concern when the cyber security of the vehicle is considered.
Types of Cyber-attacks on vehicles
Now that we are aware of what kinds of vulnerabilities exist in these automobiles, let us know further about how these vulnerabilities are used by hackers to attack:
1. Direct physical attacks. This type of attack is not possible without physical access to a vehicle. Also, the usage of physical devices like ports or connectors is required for this kind of attack. With the help of such devices, hardware is installed during the repair or renewal process of the vehicle and later the vehicle is controlled by the hacker when the normal usage process is resumed.
2. Indirect vulnerabilities in a physical attack: This is also a type of physical attack where a device with infected malware is installed into the physical vehicle. An example of this type of attack would be attacked using SD cards, USB devices, or music players.
3. Threats in a wireless attack: It involves all types of attacks that involve Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS or cellular mechanisms, etc. For this type of attack, no physical access is required.
4. Attacks using sensor fooling methods: There are ways in which sensors can be taken advantage of. Although these kinds of attacks are not very prevalent, the days are not far from where we will be dealing with these attacks if proper cyber security measures are not taken.
Below are the few types of attacks widely prevalent and used by hackers:
DOS- A DOS attack can be used to harm the user of the vehicle. It does not give any external access to the hacker but it makes the internal system of the automotive system fail. Although a hacker cannot intrude into the data or the cloud if the intention of the hacker is to harm the user, a DOS attack surely solves the purpose by making the vehicle collapse through methods like disabling the brake system.
MitM attacks-If the hacker wants to steal data from the server or intrude between the automotive and its server, the MitM attack serves the purpose. Through this type of attack, the hacker can gain access to the server.
Command injection data corruption-This type of attack is very hazardous as it uses software coding as a tool to gain access into the data stored and corrupt it.
Common steps for better cyber security in automobiles
Although cybersecurity measures must be followed all throughout the life cycle of an automotive component, below are few measures that can be followed to aid in better management of risks:
- 1. OTA refers to Over-The-Air update. Caution must be kept with interfaces such as OTA, OBD, Ethernet, and Bluetooth, basically all outside the world.
- 2. Secure all gateways related to safety and must be kept isolated or separate.
- 3. HSM refers to Hardware Security Module. It plays a significant role in delivering security services and is a major step in cyber security measures other than software-related measures.
- 4. The requirements prescribed in ISO 21434 must be followed throughout the supply-chain by all the parties across.
- 5. Cyber security framework must be followed while developing protocol stacks like UDS, SOME/IP, Flex Ray, DoIP. These must-have firewalls as an in-built function.
- 6. The ECU entry points must be deleted including all the services completely as it is a vulnerability when considered for hackers.
ISO SAE/DIS 21434
The ISO/SAE DIS 21434 is a standard jointly published by the ISO and SAE with the objective of providing a framework to organizations. The ISO 21434 is the standard when it comes to compliance for automotive cybersecurity. The ISO 21434 is for automotive cyber security as to how the ISO 26262 is for functional safety for road vehicles.
Let us get to know this standard concisely:
Cybersecurity Management: As the name suggests, this deals with the management of cyber security. It defines the aim, scope, objectives of setting the tone for cyber security through various strategies, etc.
Risk Management methods: Risk assessment is the first step in the risk management framework. Various methods to assess existing risks are explained and an analysis is conducted on existing vulnerabilities.
Concept Phase: This is the time when goals are redefined according to the extent of various automotive components exposed to risk. This aids in reducing the risks.
Product Development: This stage refers to hardware, software, and system development and the cyber security framework exclusively to be followed at this stage.
Supporting Processes: The CLAL is introduced into the activities at this stage. CLAL stands for Cybersecurity Assurance Level. CLAL in the ISO 21434 is the same as ASIL is for the ISO 26262. It is a measure which states how aggressive cybersecurity must be for a particular component.
Compliance process explained
The process of obtaiing compliance for ISO 21434 consists of three steps, which are :-
- 1. Assessment: The first step in the compliance process is risk assessment. The status and scope of risk are evaluated and a guideline is provided in a framework to be followed as a format. Before prescribing the guidelines, the compatibility to the evaluated result is thoroughly analyzed.
- 2. Implementation: After assessment comes to the implementation stage. This process includes defining the processes and procedures and roles of all the people involved in the implementation of the framework. This implementation is done keeping the ISO 21434 and its requirements in focus.
- 3. Operations: The final step towards compliance is operations, which is a continuous process. It includes controlling, assessing which would lead finally to the launch of the CSMS.

 +91 9594449393
+91 9594449393 +1 4847906355
+1 4847906355 +63 9208320598
+63 9208320598 +44 1519470017
+44 1519470017 +84 908370948
+84 908370948 +7 9639173485
+7 9639173485 +62 81808037776
+62 81808037776 +90 5441016383
+90 5441016383 +66 993367171
+66 993367171 +254 725235855
+254 725235855 +256 707194495
+256 707194495 +46 700548490
+46 700548490


