In the data dependent world today, organizations across the
globe are dealing with Personal Data in some extent or another. The increasing
number of sensitive data sharing services and platforms have raised concerns
around Personal Data and Personal Identifiable data to a great extent. Private
Data protection is an immediate need, especially for organizations that act as
PII controllers / Fiduciaries and/or PII Processors.
To address this need, Regulatory bodies across the globe have
introduced significant data privacy legislation/regulation to protect the Data
Subjects / PII Principals. The privacy specific ISO 27701:2019 standard, GDPR, California
Consumer Privacy Act and Philippines Data Protection Act are a few to name.
While going through these multiple privacy regulations
across various countries, its clear that the emphasis is more towards the
expectations from Data Processors and/or Data controls of Personal Data. These
acts/ regulations state about what the organization is supposed follow to avoid
any penalties and consequences in case of any breach or non-compliance to the
legislations. The regulations guide everyone on how to meet those expectations
in terms of Protection of the Personal data and supporting rights of data
owners etc.
ISO 27701:2019 – Extension of the renowned ISO 27001:2013
ISO 27701 specifies the requirements, providing guidance for establishing, implementing, and maintaining a privacy management system for information. The standard is an extension to ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27002.
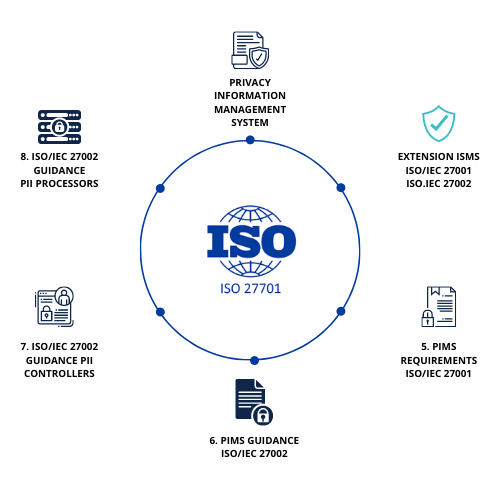
As PII controllers and PII processors hold major responsibility and accountability while managing the PII, the standard stated privacy requirements apply to all size organizations that process PII within the scope of ISMS. The clear guidance helps organizations to establish, implement, and maintain the Privacy framework within their system, helping them with the data protection measures.
The PIMS’s Clauses 5 through 8 are drafted specially for the data protection program.
Clause 5 - Data Protection: Addresses every clause in ISO 27001 and identifying organization’s status to recognize the need for data protection, considering the organization’s role in relation to PII as a controller or processor.
Clause 6: PIMS-specific guidance on ISO 27002 controls: Establishes
a top-level amendment for ‘information security’ that needs to be included
under privacy, having significantly impact on data protection.
Clause 7: Additional guidance for PII controllers: Guidance
on ISO 27701’s Annex A controls that address critical areas of data protection
and privacy that are not accounted for by the controls provided in ISO 27001.
Clause 8: Additional guidance for PII processors: Guidance
on ISO 27701’s Annex B controls addressing critical areas of data protection
and privacy that are not accounted for by the controls provided in ISO 27001.
The implementation guidance and key references stated in ISO
27701 touches base with the elements to identify:
- Impact assessment (like the kind of data the organization is collecting or processing)
- Location of the data storage (comprising of the locations impacting the data),
- Transfer of data takes place between any other parties or processing companies.
To understand these data elements better, the organization
can depend on its internal Data Flows, Process mapping documents and
more.
Meeting compliance with GDPR, CCPA, CPL
The robust guidelines and requirements stated in the ISO 27701, helps any organization implementing to come certainly halfway in meeting any other privacy legislations and regulations without much hassle. ISO 27701 provides basic requirements and guidance for the following aspects of
- Conditions for Collection and Processing of Personal Data
- Obligations towards Data Owners/ PII Principals
- How to implement Privacy by design and Privacy by default
- Conditions applied for Data Sharing, Transfer and Disclosure
Mapping with GDPR:
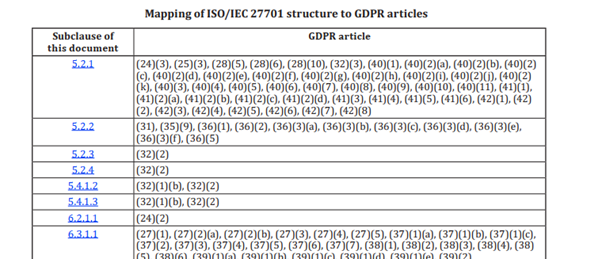
ISO 27701 Annex D, provides an indicative mapping between the requirements of GDPR and the controls stated under PIMS, indicating how fulfilling compliance as per ISO 27701 can help fulfil multiple obligations of GDPR as well.
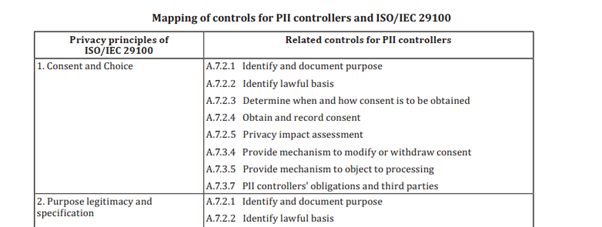
Mapping to ISO/IEC 29100 :
Annex C of the PIMS provides an indicative mapping between provisions of this document and the privacy principles from ISO/IEC 29100
Key Differences between multiple privacy standards
The main difference between various Privacy regulations/
Legislation and 27701 is that this regulation only focusses on What to do,
whereas 27701 focuses on How to do.
ISO 27701 is an auditable standard that complies with these
requirements for generating evidence of how the organization processes the
personal data. Some interesting topic while dealing with multiple privacy
standards are:
- Anonymization vs Pseudonymization
- Data Controller vs Data Processor
- Data Subject Access Request (DSAR)
- "Don't Sell My Information" on the website — Requirement of CCPA
- Backup Policy for PII
- Supervisory Authority of Member Countries
Similar affirmations hold importance while facilitating the agreements with all the stakeholders like Regulatory Bodies, End Users, Consumers, Clients and whomsoever it is relevant to.
For global organizations planning to implement privacy
controls, ISO 27701 can be the best approach for build a
baseline, even if the organizations are bound by other laws and legislations.
The prime focus should be to have stringent policies and process in place to
prevent fines owing to data breach or non-compliance with the data protection
regulations.
As ISMS is the prime requirement to build your information
security management, investing in international privacy standard like PIMS (ISO
27701) will certainly have a positive impact in long term.

 +91 9594449393
+91 9594449393 +1 4847906355
+1 4847906355 +63 9208320598
+63 9208320598 +44 1519470017
+44 1519470017 +84 908370948
+84 908370948 +7 9639173485
+7 9639173485 +62 81808037776
+62 81808037776 +90 5441016383
+90 5441016383 +66 993367171
+66 993367171 +254 725235855
+254 725235855 +256 707194495
+256 707194495 +46 700548490
+46 700548490


