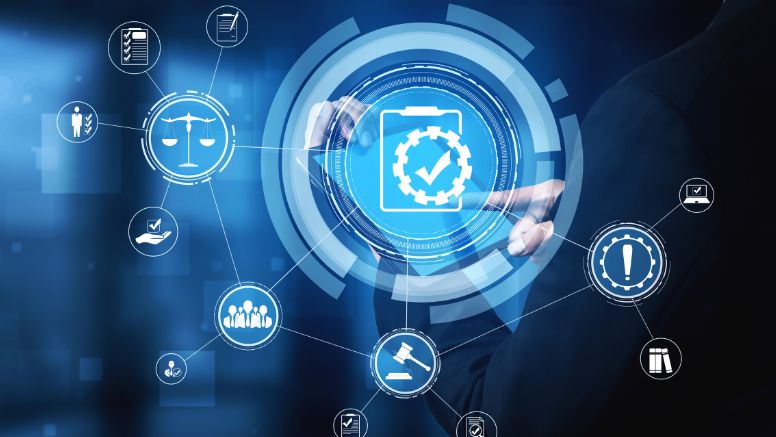
On August 1, 2024, the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) introduced new Information and Cybersecurity Guidelines for regulated entities and intermediaries. These guidelines, which took effect immediately, aim to enhance the security and integrity of the evolving digital architecture and safeguard subscribers' interests.
Key highlights of the guidelines include:
- Cyber Risk Management : The guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for regulated entities to effectively manage cyber risks, protect critical assets, and maintain trust in a digital environment. This serves as a roadmap for entities to bolster their cybersecurity measures in response to emerging threats.
- Security Standards and Procedures : The guidelines establish a broad standard to help regulated entities understand and implement essential controls and procedures. This is aimed at protecting their Information and Communication Technology (ICT) infrastructure from cyber threats, enhancing overall resilience.
- Governance Structure : The guidelines mandate the establishment of a robust governance framework, including the creation of an Information and Cybersecurity Risk Management Committee (ICSRM). This committee, comprising a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), Chief Risk Officer (CRO), Chief Technology Officer (CTO), and other functional heads, will oversee cybersecurity policies, approve security projects, and monitor incident response activities.
- Cybersecurity Audits and Compliance : Regulated entities are required to conduct regular cybersecurity audits, including internal and external audits, to assess their security posture against the guidelines. External audits must be performed by CERT-In empaneled cybersecurity auditors at least once a year, with internal audits conducted biannually to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Incident Response and Recovery : The guidelines emphasize the need for a robust Cyber Crisis Management Plan (CCMP) to ensure quick detection, containment, and mitigation of cybersecurity incidents. Regulated entities must have clear response and recovery procedures, including incident classification, communication strategies, and root cause analysis to minimize operational impacts.
- Baseline Security Measures : The guidelines outline baseline security measures such as access controls, network security management, data encryption, and application security practices. These measures are intended to protect critical systems and data from unauthorized access, malware attacks, and other cyber threats.
- Periodic Review and Updates : The information and cybersecurity policy of regulated entities must be reviewed and updated at least once every two years. This review should take into account changes in regulatory requirements, technological advancements, and lessons learned from previous incidents to continuously improve security measures.
- Capacity Management and Disaster Recovery : Regulated entities are required to maintain a robust Business Continuity Plan (BCP) and Disaster Recovery Management (DRM) policy. The guidelines mandate periodic testing of these plans to ensure they are effective in supporting the organization’s resilience objectives and enable rapid recovery from cyberattacks or other disruptions.
- Protection of Critical Information Assets : Entities are required to identify and classify their critical information assets and implement appropriate security measures such as Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT), data encryption, and secure application development practices.
These guidelines demonstrate PFRDA’s commitment to bolstering cybersecurity in the financial sector, ensuring that regulated entities are equipped to safeguard sensitive data and maintain the integrity of their operations in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Read the full circular here : https://www.pfrda.org.in/myauth/admin/showimg.cshtml?ID=3202

 +91 9594449393
+91 9594449393 +1 4847906355
+1 4847906355 +63 9208320598
+63 9208320598 +44 1519470017
+44 1519470017 +84 908370948
+84 908370948 +7 9639173485
+7 9639173485 +62 81808037776
+62 81808037776 +90 5441016383
+90 5441016383 +66 993367171
+66 993367171 +254 725235855
+254 725235855 +256 707194495
+256 707194495 +46 700548490
+46 700548490


