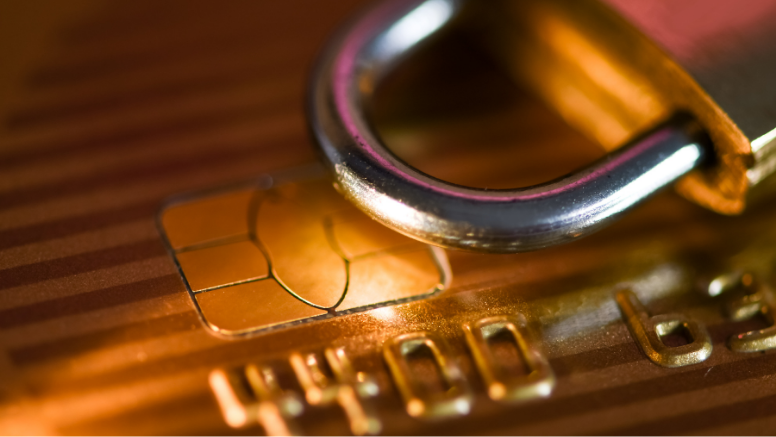
Understand the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard requirements and how the critical role it plays under placing a robust benefit on successful enforcement of the PCI DSS compliance program.
Developed and launched by the founding payment brands of PCI Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) in 2006, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a standardized, industry-wide set of requirements and processes for security management, policies, procedures, network architecture, software design, and critical protective measures.
The requirements stated for PCI DSS compliance are essential to ensure that all entities that process, store, or transmit payment card information maintain a secure environment to prevent any security incident. Though the PCI DSS is not a law, it holds a strong contractual obligation to be applied and enforced through fines or other restrictions – directly by the payment providers themselves.
Here we will have a look at :
- Overview of the PCI DSS
- 12 Requirements for PCI DSS compliance
- PCI compliance Benefits
- Difficulties Posed by PCI Non-Compliance
- Conclusion
PCI DSS Implementation does not require any special grade countermeasures but focuses on placing a minimum baseline to help organizations defend their business against their attackers.
Aiding the successful implementation of the PCI DSS compliance program, the PCI SSC council has provided a set of resources to aid any organization that seeks to implement or attain PCI DSS compliance. Along with other key documents, the security council has provided:
- PCI Data Security Standard quick reference guide and approach
- PCI Software Security Framework and a list of Validated Payment vendors and applications under its Secure Software Standard and Secure Software Lifecycle Standard to help payment software vendors adhere to security practices in the development cycle and software.
- PCI PIN Transaction Security (PTS) requirements for device vendors and manufacturers, along with a list of approved PIN transaction devices
- Self-Assessment Questionnaires templates in aiding organizations to validate their PCI DSS compliance.
- List of Qualified Security Assessors (QSAs) for the multiple compliance standards
- List of Approved Scanning Vendors (ASVs)
- An Internal Security Assessor (ISA) education program
The council also provides resources for Card production, PIN, TSP (Token Service Providers), and contactless payments, etc.
12 Requirements for PCI DSS compliance
The PCI DSS compliance program has seen major changes over the years, The latest versions groups the 12 PCI DSS requirements, in the six principles stated are as follows:
Implementation of Secure Network Infrastructure
- Install and maintain a secure firewall
Network firewalls can be software or hardware technologies that provide the first line of defense to a network. Firewalls can restrict incoming and outgoing network traffic
through rules and criteria configured by your organization. Being the first line of defense against cyber threats and their effectiveness, firewalls are required for PCI DSS compliance. - Password protection policy
Implementation of adequate configuration standards for networking devices and applications in the enterprise is necessary. Using third-party products with generic passwords lowers the effectiveness of the security measures, making the systems easily accessed by the public. IT heads need to maintain and update asset inventory along with a strict policy for password usage and configuration, to ensure PCI DSS compliance.
Secure Cardholder Data - Protect Cardholder data
The third requirement is designed to minimize the impact of an attacker managing to compromise your network and system components to gain unauthorized access to your data stores. To effectively reduce the risk of unauthorized access, it is necessary that data retention is kept to an absolute minimum and the stored data is protected using Encryption, Tokenization (with effective supporting practices), and so on.
Regular scanning and maintenance of the cardholder data environment are required to ensure that no unencrypted data exists, to maintain PCI DSS compliance. - Encrypt cardholder data across the network
Much like "Cash In Transit," cardholder data is sent across multiple channels as per requirement. This makes it necessary to ensure that the sensitive cardholder data is encrypted when transiting over public-facing environments.
Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program - Install and maintain an antivirus program
Cybercriminals are constantly evolving malware strains, hence all the devices that require an antivirus program must be installed. The program needs to be patched and updated regularly. With evolving security requirements, it's essential that asset security programs remain updated and to ensure that the controls remain effective.
The audit logs help you to verify compliance with PCI DSS assessment, without which one would be unaware of an unauthorized browser extension or malware that can read PANs as they are entered into a payment application. - Maintain strong system and application
Application developers can never be perfect hence it is necessary to update/patch security holes, a cybercriminal will pass the security vulnerabilities across the hacker community to exploit the weakness until the systems are patched. The software development process must be carried out securely to ensure no new vulnerabilities are introduced.
All changes must be managed, to document the supporting risk-based
decisions made (e.g., Impact, Rollback options, etc. The updates are necessary for all software on devices that are used to manage cardholder data.
Implement Strong Access Control Measures - Restrict access to cardholder data
Isolating access rights is nowhere crucial than the payment cardholder data. The merchants need to ensure that managing employees grant access rights to the least amount of data that are necessary to perform any action.
It's necessary to establish an access control system for each element of the cardholder data infrastructure, and all access rights must be set by default to ‘deny all’ unless an individual is specifically allowed access to designated cardholder data. - Authentication policy for access to system components
Any person who has access to cardholder data should have individual credentials for access identification. Unique IDs and authentication methods (passwords/token devices/biometrics) should be used for everyone. Prohibit shared/generic accounts and implement Two-factor authentication for remote access. - Restrict physical access
Merchants need to restrict physical access to cardholder data or systems that house cardholder data – including hardcopies, stored in a secure location to manage PCI DSS compliance.
The card environment should have physical security controls and procedures for the identification and management of any visitors to the premises.
Regularly Monitor and Test Networks - Monitor and maintain access logs
All activities concerning handling and managing cardholder data need to have a log entry associated with them. The logging mechanisms are necessary for vulnerability management. Merchants must create a process that links all access by individual users to
cardholder system components that will enable you to reconstruct and record events.– especially when done with administrative privileges.
The ability to produce detailed audit reports on demand is important for PCI DSS compliance. - Regularly test security systems and processes
New vulnerabilities are discovered daily and hence PCI DSS requires merchants to regularly test cardholder data systems and processes to find those vulnerabilities and fix them. Vulnerability scans for both internal and external networks (at least quarterly) and penetration testing (network and application layer) are required.
Network and host-based IDS or IPS are to be managed and maintained along with a system to monitor file integrity.
Maintain an Information Security Policy - Document and maintain policies that address information security for all personnel
PCI DSS compliance requires merchants to maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel. The policies determine the nature of the controls used to ensure security and comply with PCI requirements that apply to each component in the cardholder data environment like – PIN entry devices, servers, network services, applications, PCs, and other endpoints.
PCI Compliance Benefits
Cybercriminals are opportunists that seek to exploit the misinterpretation/misapplication of the PCI DSS controls, poorly managed PCI DSS oversight, bad practices, or poor risk management processes. Even though the process of complying is a very daunting task, yet its importance is growing over time. The process of gaining PCI DSS compliance with the right tools can be completed with ease even considering the maze of standards and issues.
The compliance benefits can be counted as follows :
- Ensure system security and develop customer trust, confidence and manage system security that ensures trust for businesses
- Reduce the risk of security breaches by ensuring application security and loophole closure concerning Cardholder Date and Cardholder Data Environment.
- An increase in business prospects as being the PCI compliance stature promotes one as a secure business ensuring growth in reputation.
- An organization that complies with PCI DSS should be able to decrease the data breach significantly. Being compliant with PCI DSS ensures that the company has a strong commitment to protecting its data, improving customer relationships.
- Gaining PCI DSS compliance will prepare you better with other privacy and regulation standards like ISMS,HIPAA, SOX, GDPR, etc.
- Successful implementation will lead to the overall improvement of IT infrastructure efficiency.
Difficulties Posed by PCI Non-Compliance
PCI DSS compliance is treated as an annual "tick box" audit however, this is far from reality where PCI DSS should be treated more like having the responsibility for owning and running couriers, road haulage, or taxi services. The increasing dependency on electronic payment systems has increased its regard in the eyes of cybercriminals. This ever-growing trend toward payment cards increases the potential opportunities for criminals to exploit poor practices.
Failing to noncompliance would result into :
- Data breach incidents that affect consumers, financial institutions along with severe damage to the company brand.
- In addition to the loss of brand reputation, a merchant should expect their revenue to drop drastically owing to the loss of clients followed by a security incident.
- Legal actions, insurance claims. government fines and lawsuits and canceled accounts.
Conclusion
The PCI DSS compliance poses a challenge to every business that's not rightly prepared and looking forward to gaining the PCI DSS compliance status. PCI DSS continues to evolve based upon mature and well-established industry best practices. Consequently, to repay the consumer trust and to reduce the attractiveness to criminals, businesses must understand the heritage of the PCI DSS controls to better enable them to develop robust defenses.

 +91 9594449393
+91 9594449393 +1 4847906355
+1 4847906355 +63 9208320598
+63 9208320598 +44 1519470017
+44 1519470017 +84 908370948
+84 908370948 +7 9639173485
+7 9639173485 +62 81808037776
+62 81808037776 +90 5441016383
+90 5441016383 +66 993367171
+66 993367171 +254 725235855
+254 725235855 +256 707194495
+256 707194495 +46 700548490
+46 700548490


