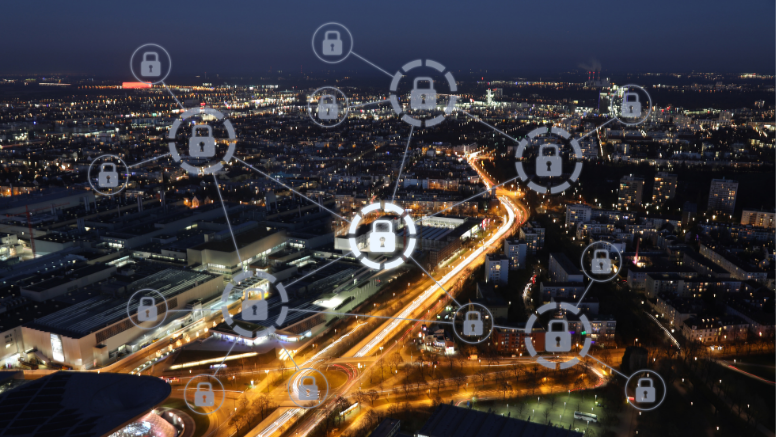
Establish Cyber Security Baseline and Resilience

With the ever-increasing cyberthreat landscape and the rising data breaches, the financial and information systems need to be under tighter security controls. The traditional compliance requirements are failing to meet the growing sophistication of the cyberattacks today, and hence businesses and governments organizations need to ensure that they are on the forefront of defending these advanced adversaries.
In 2011, the central banking institution released extensive IT security guidelines, but it felt compelled to update its guidance partly as the original advisory didn’t sufficiently address the need for post-breach capabilities. The RBI’s Cybersecurity Framework in Banks is one such step towards safeguarding the crucial business assets, ensuring security compliance and data integrity.
The RBI’s Cybersecurity Framework defines requirements for today’s modern financial organization to protect themselves from the evolving attack techniques developed by cyber attackers every day. The framework addresses three core areas namely:-
-
-
Operate Cyber Security Operations Centre
-
Cyber Security Incident Reporting (CSIR).
The Baseline Cyber Security and Resilience Requirements consists of:-
-
Need for a Board approved Cyber-security Policy
-
Cyber Security Policy to be distinct from the broader IT policy / IS Security Policy of a bank
-
Arrangement for continuous surveillance
-
IT architecture should be conducive to security
-
Comprehensively address network and database security
-
Comprehensively address network and database security
-
Ensuring Protection of customer information
-
Cyber Crisis Management Plan
-
Cyber security preparedness indicators
-
Cyber Crisis Management Plan
-
Sharing of information on cyber-security incidents with RBI
-
Supervisory Reporting framework
-
An immediate assessment of gaps in preparedness to be reported to RBI
-
Cyber-security awareness among stakeholders / Top Management / Board
After having an efficient surveillance system, the framework outlines the need to:
-
Operate Cyber Security Operations Centre:
-
Cyber Security Incident Reporting (CSIR):
The Cyber SoC must take into account proactive monitoring and management capabilities with sophisticated tools for detection, quick response and backed by data and tools for sound analytics. The guidelines specifically call out the use of honeypot services. This is one of the very few specifications of a particular technology by the framework, which speaks to the clear value of honeypot solutions in detecting and responding to advanced threats.
Banks are stated to promptly notify RBI of any or all “unusual” cyber-security incidents whether successful or not. The notification can take no more than 6 hours, which means that detection and analysis must take place extremely quickly.
The Incident Report plan includes a Cyber Crisis Management Plan (CCMP), addressing Incident Detection, Response, Recovery and Containment.

 +91 9594449393
+91 9594449393 +1 4847906355
+1 4847906355 +63 9208320598
+63 9208320598 +44 1519470017
+44 1519470017 +84 908370948
+84 908370948 +7 9639173485
+7 9639173485 +62 81808037776
+62 81808037776 +90 5441016383
+90 5441016383 +66 993367171
+66 993367171 +254 725235855
+254 725235855 +256 707194495
+256 707194495 +46 700548490
+46 700548490
